The projects from the Sustainable Built Environments Research Area addresses sustainability, circular economy, social equity, and digital innovation in the built environment. Efforts span from improving plastic circularity and reclaiming materials to integrating advanced modeling tools and AI for energy-efficient urban planning. Several projects focus on user behavior and well-being in buildings, with others target social sustainability through neighbourhood design and sharing economy frameworks. EU-funded initiatives contribute strategies to tackle housing inequality and promote climate resilience. Collectively, the research supports a data-driven, inclusive transition toward circular, energy-efficient, and socially responsive cities.

Ongoing

Improving plastic circularity in the construction sector
This project aims to improve plastic waste management at the construction sites to improve the plastic circularity, bringing the climate incentives into focus.

Exploring the material stock – urban form nexus for urban sustainability
This project uses a systems perspective to include, understand, and analyze interrelations between built environment material stocks, morphological types (e.g., buildings, roads), their spatial characteristics, the function they provide (e.g., shelter, transport), and socioeconomic and environmental implications of different urban forms. At the core of this project is the integration of two disciplines with a strong systems perspective tradition: built environment stock modeling and urban morphology.

Future Urban Resource Centers
The development of buildings is an immensely carbon- and resource-intensive process and circular economy strategies are key to decrease the environmental impacts of the construction industry. In developed economies, extensive volumes of construction materials are stocked in existing buildings and ought to be reclaimed.

Digital material inventories for sustainable urban mining
This project develops a method to enable the reuse and recycling of urban construction materials using urban digital twins. By combining remote sensing, computer vision, and machine learning, it creates a detailed, dynamic inventory of material stocks to support circular economy strategies and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The approach advances life cycle assessment methods and will be tested through real-world case studies with stakeholder input.

EqualHouse
From housing inequality to sustainable, inclusive and affordable housing solutions.

Users’ impact on domestic energy consumption
The project aims to improve the understanding of the impact of users on domestic energy use by conducting a pilot study in the HSB Living Lab, and develop a methodology to study the impact of occupants’ physiological and behavioural responses on their home’s energy use.
Completed

DecarbonAIte
The DecarbonAIte project aims to extract data on building characteristics from public databases. Use this information to elaborate and reinforce urban digital twin models. Finally, through this platform, to propose optimal renovation measures. The system to be implemented targets various stakeholders, from building owners to policy makers.

Architectural design variable assessment in multi-objective life cycle optimisation
This project aims to identify the important architectural design variables in early design stage for life cycle optimisation by interacting with stakeholders who have major influence in early design stage.
Digitalisation of social sustainability in neighbourhood design
Digital tools for performance-assessment are commonly used to shorten the feedback loop in testing designs for buildings and neighbourhoods. However, these tools do not extend to the social dimension in the same way as the economic and environmental dimensions. The aim of this project is to develop a theoretical understanding of social sustainability at the neighbourhood planning level and propose a model for the development of digital tools.

Sustainable Bridges
This project aims at the full utilization of the benefits offered by stainless steel to have sustainable and “maintenance-free” road bridges which have competitive investment costs to that of their traditional carbon steel counterparts. It is believed that by the use of bridge girders with corrugated webs and stainless steel reinforcement and optimization of the material usage and production costs, a considerable reduction in the investment costs of a stainless-steel solution is attainable.

Twinable
A multiscale design interaction and visualization approach using mixed realities.

CREATE
The CREATE project aimed at supporting urban transformation processes towards the circular economy by developing a tool (CREATE tool) that makes an inventory of the existing material stocks in the built environment and explores scenarios for future expected material flows from renovation and demolition activities.

Holistic life cycle performance optimization
The main goal of the project is to mainstream holistic life cycle performance optimisation in early design stages of buildings to save energy and greenhouse gas emissions. All performance optimisation will follow a life cycle perspective.
REDAP
The aim of this project is to develop a Regional Energy Demand Analysis Portal (REDAP) together with the partner countries Austria, Ireland and Sweden based on local and regional Need-owners demands.

SEsam
SEsam : Sharing Economy sustainability assessment method to support the implementation of sharing economy initiatives at neighbourhood level. The aim of this project is to develop and apply a systemic method that quantifies the sustainability benefits of implementing different sharing economy initiatives in neighborhoods in cities.

Occupant well-being and productivity in sustainable office buildings
The project aims to develop advanced indoor environmental quality IEQ in sustainable office buildings promoting occupant comfort, health, and productivity by identifying key factors and revealing causal relations from evidence-based studies. A national dataset will be aggregated from the office buildings in Sweden by physical measurement and subjective survey.

Urban modelling and planning tool for energy and invisible environmental factors using AI methods
To plan, build or renovate cities, engineers and decision makers need tools and workflows that are compartmentalized and work ad-hoc without correlating different parameters. To tackle these problems and enable environmental assessment and policy analysis, this project aims to create an urban modeling planning tool for the energy demand of buildings and the invisible environmental factors of noise and wind. The project will . * provide a basis for scenario analysis of any urban area in Sweden. * use AI/ML to enrich existing models . * make the toolsets readily available, and. * enable improved visualization and communication or results.
WELL Neighbourhood
This project is about developing digital tools to promote social sustainability in neighbourhood design.

Energy performance and occupant satisfaction in green-certified office buildings
The project aims to reflect on green building design and operation and occupant satisfaction and experience in the “real world”; explore the potential causes from the detailed design parameters, necessary conditions in the building certification scheme and building operation and control.
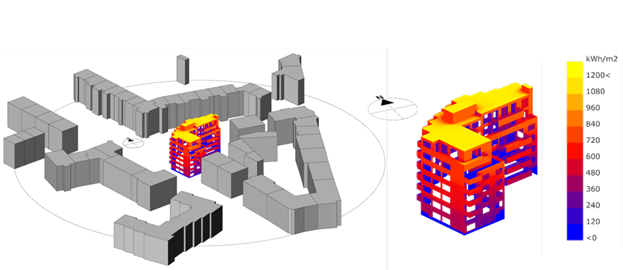
Powering the City
Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) offers renewable energy to be generated on-site and prevents additional sealing of natural ground, potentially replacing traditional building elements. The objective of the Powering the City module is to develop a holistic, multi-scale and interdisciplinary approach for assessing large scale deployment of BIPV in urban contexts under different climatic, socio-economic and architectural / urban conditions. The team will use Zurich and Singapore as exemplary and complementary case studies.
